Hyperparameter Tuning and Experiment Tracking
This project focuses on Hyperparameter Optimization for a CatDog Classification model, leveraging powerful tools like Aim, MLflow, DVC, CML, Hydra, and Optuna. It demonstrates how to streamline experiment tracking, model tuning, and reporting with modern ML tools.
Table of contents
Overview
This repository applies hyperparameter optimization techniques. It uses a sample dataset of 100 images per class from the Chest X-Ray Pneumonia dataset, and integrates cutting-edge ML tools to automate experiment tracking, model training, and reporting.
Tools and Frameworks
Aim

It is an open-source tool designed for experiment tracking and visualization. It provides fast and efficient tracking for large-scale experiments, with an interactive web-based dashboard to compare runs.
Key Features:
- Lightweight and scalable experiment tracking.
- Rich visualizations for metrics and hyperparameter tuning.
- Easy to integrate with frameworks like PyTorch and TensorFlow.
Commands:
- Start Aim dashboard:
aim up - Run an experiment and track metrics:
aim run python src/train.py experiment=<experiment_name>
MLflow
It is an open-source platform for managing the end-to-end machine learning lifecycle, including experimentation, model packaging, and deployment.
Key Features:
- Logs parameters, metrics, and artifacts.
- Provides a model registry to store and version models.
- Powerful UI for visualizing and comparing multiple runs.
Commands:
- Start the MLflow UI:
mlflow ui - Run an experiment and log metrics:
mlflow run . --experiment-name "<experiment_name>"
DVC

DVC (Data Version Control) is a version control system tailored for machine learning projects, handling datasets and models.
Key Features
- Manages datasets and models with Git-like version control.
- Integrates with cloud storage like Google Drive, AWS S3, and Azure.
- Ensures reproducibility across experiments by tracking datasets and models.
Commands:
- Install dependencies and pull the dataset:
UV_EXTRA_INDEX_URL=https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu uv sync - Pull the data from DVC:
uv run dvc pull
Continuous Machine Learning (CML)

It integrates machine learning workflows into GitHub Actions or GitLab CI, automating the entire pipeline.
Key Features:
- Automates ML pipelines within CI/CD systems.
- Generates reports for each experiment.
- Supports model evaluation and metrics reporting directly in GitHub/GitLab.
Commands:
- Create reports and post results automatically during CI runs:
uv run python scripts/generate_results.py
Hydra
Hydra is a framework for managing complex configurations in machine learning experiments. It simplifies running multiple configurations and allows you to easily override settings on the command line.
Key Features:
- Dynamic configuration management for complex projects.
- Supports multirun for running multiple experiments simultaneously.
- Easily override configuration values from the command line.
Commands:
- Run a training script with configuration overrides:
python src/train.py experiment=<experiment_name> +trainer.fast_dev_run=True - Run multiple experiments with different configurations:
python src/train.py --multirun experiment=<experiment_name> model.embed_dim=16,32,64 +trainer.log_every_n_steps=5
Optuna

Optuna is an open-source hyperparameter optimization framework designed to efficiently search hyperparameter spaces for the best configurations.
Key Features:
- Efficient hyperparameter search using techniques like Bayesian optimization.
- Parallelization for faster search.
- Visualizations to help analyze search results.
Commands:
- Run a hyperparameter search with Optuna:
python src/train.py --multirun hparam=catdog_vit_hparam +trainer.log_every_n_steps=5 hydra.sweeper.n_jobs=4
Hyperparameter Tuning Results
Combined Metrics Plot
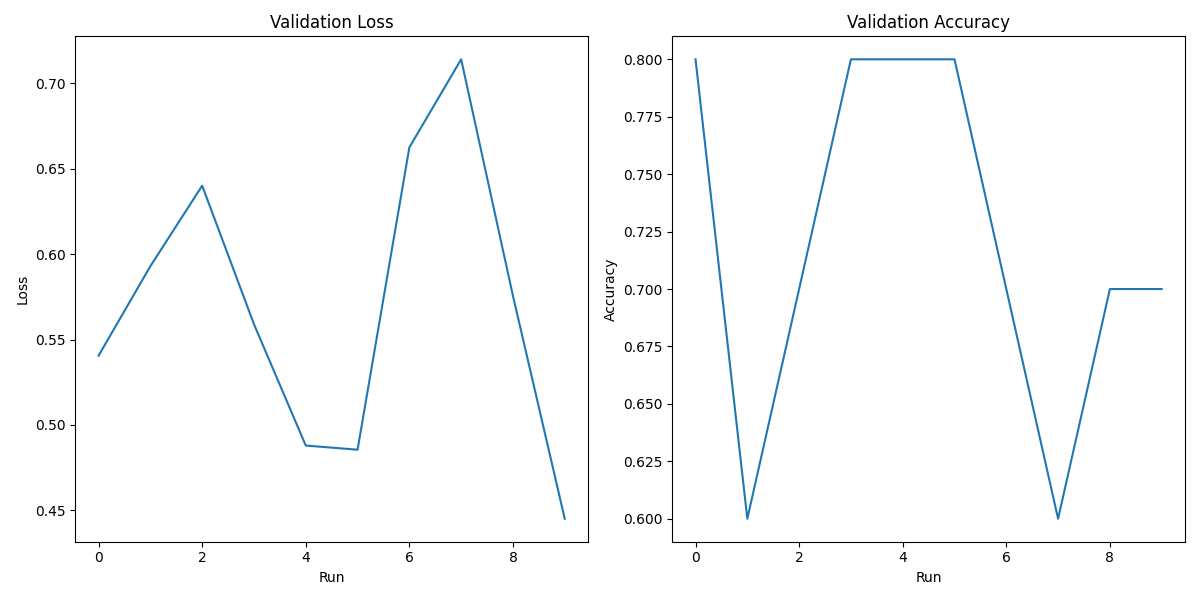
Best Hyperparameters
| Parameter | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | name | optuna |
| 1 | model.drop_path_rate | 0.2089407556793585 |
| 2 | model.head_init_scale | 0.9292090024255693 |
| 3 | model.lr | 0.00023458293902856107 |
| 4 | model.weight_decay | 0.0005513192559352005 |
| 5 | data.batch_size | 64 |
| 6 | augmentation.horizontal_flip | True |
| 7 | augmentation.random_crop | True |
| 8 | augmentation.random_rotation | True |
| 9 | regularization.gradient_clipping | 0.15371010694861154 |
| 10 | best_value | 1.0 |
Hyperparameters for Each Experiment
| base_model | num_classes | pretrained | lr | optimizer | weight_decay | scheduler_patience | scheduler_factor | drop_path_rate | head_init_scale | horizontal_flip | random_crop | random_rotation | val_acc | val_loss | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | convnext_nano | 2 | False | 0.0003 | AdamW | 0.0010 | 3 | 0.1000 | 0.2257 | 0.6574 | True | True | True | 0.8000 | 0.5406 |
| 1 | convnext_nano | 2 | False | 0.0002 | AdamW | 0.0006 | 3 | 0.1000 | 0.2089 | 0.9292 | True | True | True | 0.6000 | 0.5929 |
| 2 | convnext_nano | 2 | False | 0.0005 | AdamW | 0.0007 | 3 | 0.1000 | 0.0723 | 1.0152 | True | True | True | 0.7000 | 0.6401 |
| 3 | convnext_nano | 2 | False | 0.0004 | AdamW | 0.0000 | 3 | 0.1000 | 0.2775 | 1.7625 | True | True | True | 0.8000 | 0.5590 |
| 4 | convnext_nano | 2 | False | 0.0002 | AdamW | 0.0002 | 3 | 0.1000 | 0.1194 | 1.6070 | True | True | True | 0.8000 | 0.4880 |
| 5 | convnext_nano | 2 | False | 0.0003 | AdamW | 0.0009 | 3 | 0.1000 | 0.2148 | 0.5226 | True | True | True | 0.8000 | 0.4855 |
| 6 | convnext_nano | 2 | False | 0.0009 | AdamW | 0.0005 | 3 | 0.1000 | 0.1251 | 1.5220 | True | True | True | 0.7000 | 0.6624 |
| 7 | convnext_nano | 2 | False | 0.0009 | AdamW | 0.0003 | 3 | 0.1000 | 0.0952 | 1.1222 | True | True | True | 0.6000 | 0.7140 |
| 8 | convnext_nano | 2 | False | 0.0001 | AdamW | 0.0004 | 3 | 0.1000 | 0.0881 | 1.4465 | True | True | True | 0.7000 | 0.5756 |
| 9 | convnext_nano | 2 | False | 0.0006 | AdamW | 0.0007 | 3 | 0.1000 | 0.0287 | 1.8280 | True | True | True | 0.7000 | 0.4451 |
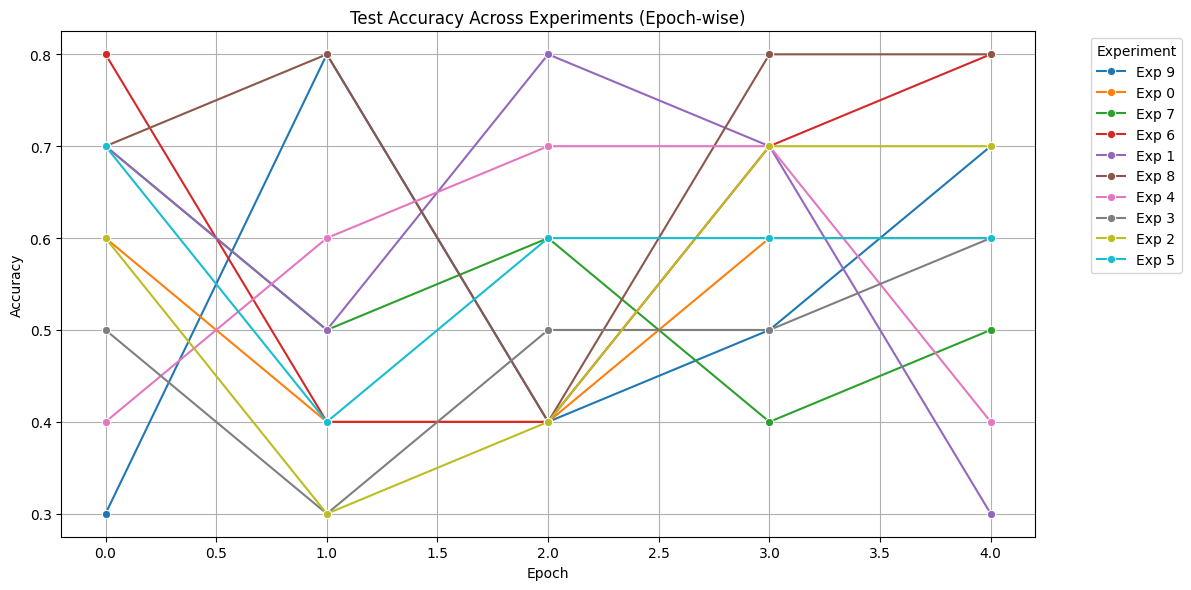
Test Accuracy Across Experiments (Epoch-wise)