Deploying and Benchmarking Image Classifier with LitServe
Table of contents
Introduction to LitServe
LitServe is a lightweight framework designed for serving machine learning models with high performance and scalability. It simplifies the deployment of models, allowing developers to focus on building and optimizing their applications. With LitServe, you can easily expose your models as APIs, enabling seamless integration with various applications.
pip install litserve
Why LitServe?
LitServe vs Other Frameworks
- Ease of Use: Simple to set up and deploy.
- Performance: High throughput with minimal latency.
- Batching: Built-in support for batching, ensuring efficient GPU utilization.
LitAPI
Key Lifecycle Methods
setup(): Initializes resources when the server starts. Use this to:- Load models
- Fetch embeddings
- Set up database connections
decode_request(): Converts incoming payloads into model-ready inputs.predict(): Runs inference on the model using the processed inputs.encode_response(): Converts predictions into response payloads.
Unbatched Requests
The above methods handle one request at a time, ensuring low-latency predictions for real-time systems.
Batched Requests
Batching processes multiple requests simultaneously, improving GPU efficiency and enabling higher throughput. When batching is enabled:
- Requests are grouped based on
max_batch_size. - decode_request() is called for each input.
- The batch is passed to the
predict()method. - Responses are divided using unbatch() (if specified).
LitServer
LitServer is the core of LitServe, managing:
- Incoming requests
- Parallel decoding
- Batching for optimized throughput
Hands-On with LitServe
Step 1: Start an EC2 Instance on AWS
- Instance type: g6.xlarge
- Activate your environment:
source activate pytorch
Verify GPU availability using nvidia-smi:
Step 2: Deploy the Image Classifier
Run the server script:
python aws-litserve/server.py
Step 3: Benchmark Performance
Evaluate the server’s performance with:
python aws-litserve/benchmark.py
Server
import torch
import timm
from PIL import Image
import io
import litserve as ls
import base64
import boto3
import rootutils
from timm_classifier import TimmClassifier
class ImageClassifierAPI(ls.LitAPI):
def setup(self, device):
"""Initialize the model and necessary components"""
self.device = device
# Load model from S3
s3 = boto3.client('s3')
bucket_name = 'mlops-aws'
model_key = 'model/cat_dog_model.ckpt'
# Download the model file from S3
model_file = 'cat_dog_model.ckpt'
# s3.download_file(bucket_name, model_key, model_file)
# Load the model from checkpoint
self.model = TimmClassifier.load_from_checkpoint(model_file) # Load model from checkpoint
self.model = self.model.to(device)
self.model.eval()
# Get model specific transforms
data_config = timm.data.resolve_model_data_config(self.model)
self.transforms = timm.data.create_transform(**data_config, is_training=False)
# Load class labels
self.labels = ["Cat", "Dog"]
def decode_request(self, request):
"""Convert base64 encoded image to tensor"""
image_bytes = request.get("image")
if not image_bytes:
raise ValueError("No image data provided")
# Decode base64 string to bytes
img_bytes = base64.b64decode(image_bytes)
# Convert bytes to PIL Image
image = Image.open(io.BytesIO(img_bytes))
# Convert to tensor and move to device
tensor = self.transforms(image).unsqueeze(0).to(self.device)
return tensor
@torch.no_grad()
def predict(self, x):
outputs = self.model(x)
probabilities = torch.nn.functional.softmax(outputs, dim=1)
return probabilities
def encode_response(self, output):
"""Convert model output to API response"""
# Get top 5 predictions
probs, indices = torch.topk(output[0], k=5)
return {
"predictions": [
{
"label": self.labels[idx.item()],
"probability": prob.item()
}
for prob, idx in zip(probs, indices)
]
}
if __name__ == "__main__":
api = ImageClassifierAPI()
server = ls.LitServer(
api,
accelerator="gpu",
)
server.run(port=8000)
Client
import requests
from urllib.request import urlopen
import base64
import boto3
def test_single_image():
# Get test image from S3
s3_bucket = 'mlops-aws'
s3_key = 'input-images/sample-iamge.jpg' # Replace with the path to your image in S3
s3 = boto3.client('s3')
img_data = s3.get_object(Bucket=s3_bucket, Key=s3_key)['Body'].read() # Fetch image from S3
# Convert to base64 string
img_bytes = base64.b64encode(img_data).decode('utf-8')
# Send request
response = requests.post(
"<http://localhost:8000/predict>",
json={"image": img_bytes} # Send as JSON instead of files
)
if response.status_code == 200:
predictions = response.json()["predictions"]
print("\\nTop 5 Predictions:")
for pred in predictions:
print(f"{pred['label']}: {pred['probability']:.2%}")
else:
print(f"Error: {response.status_code}")
print(response.text)
Image Processing Workflow
- Decode: Convert base64 images to tensors.
- Predict: Run inference using
softmaxprobabilities. - Encode: Return top predictions with their probabilities.
Benchmarking the API
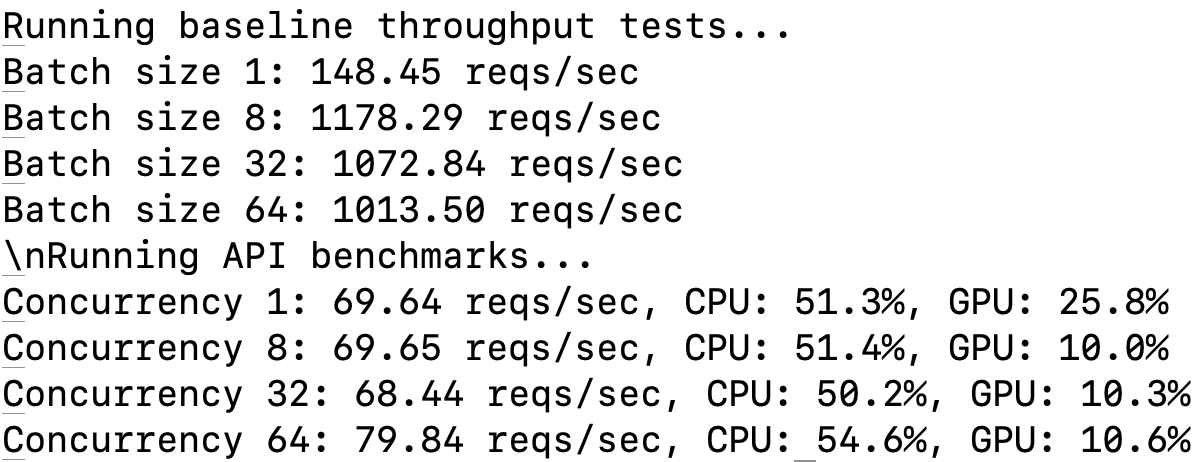
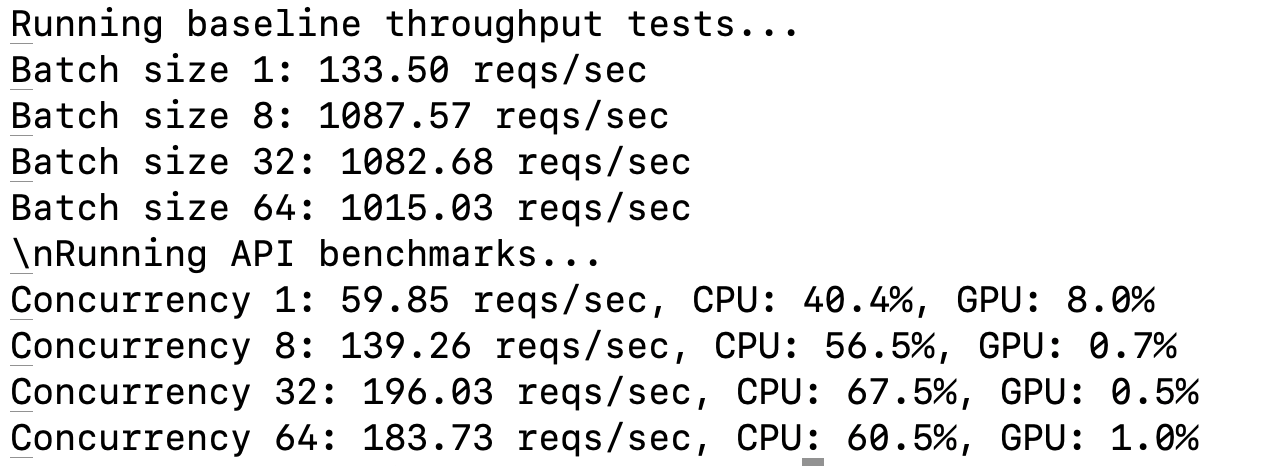
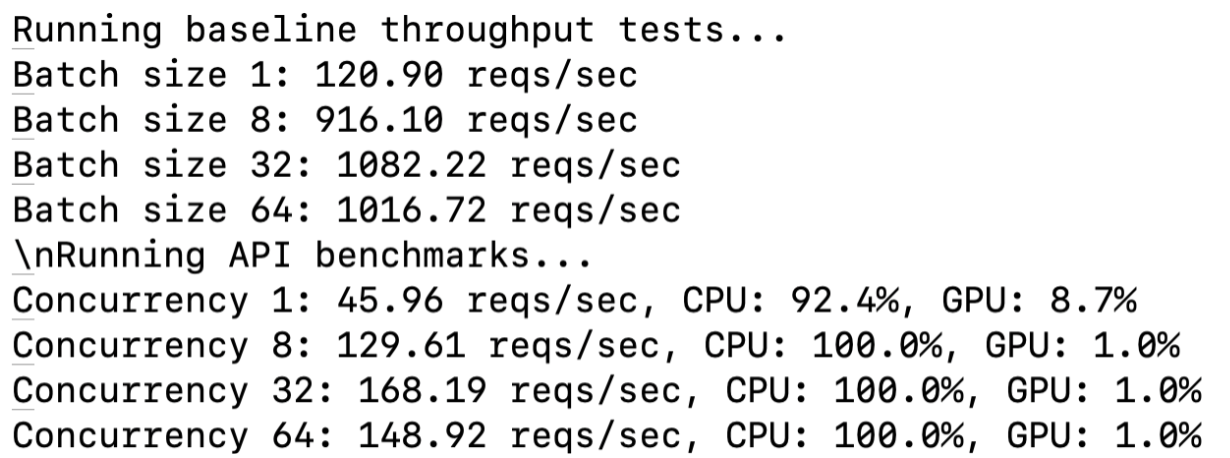
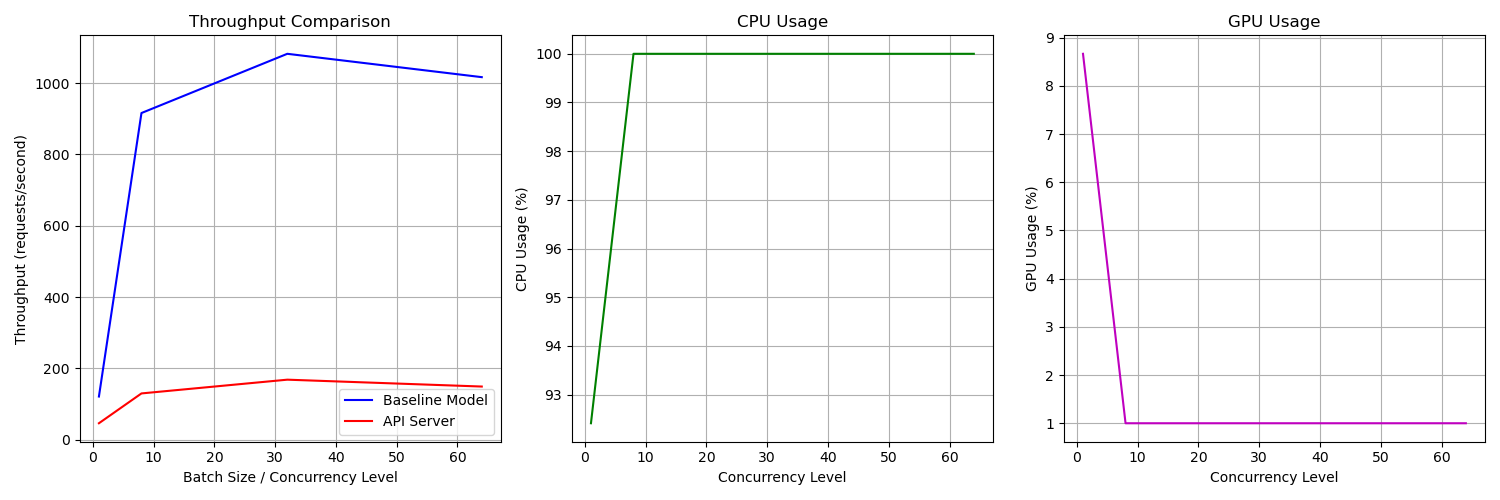
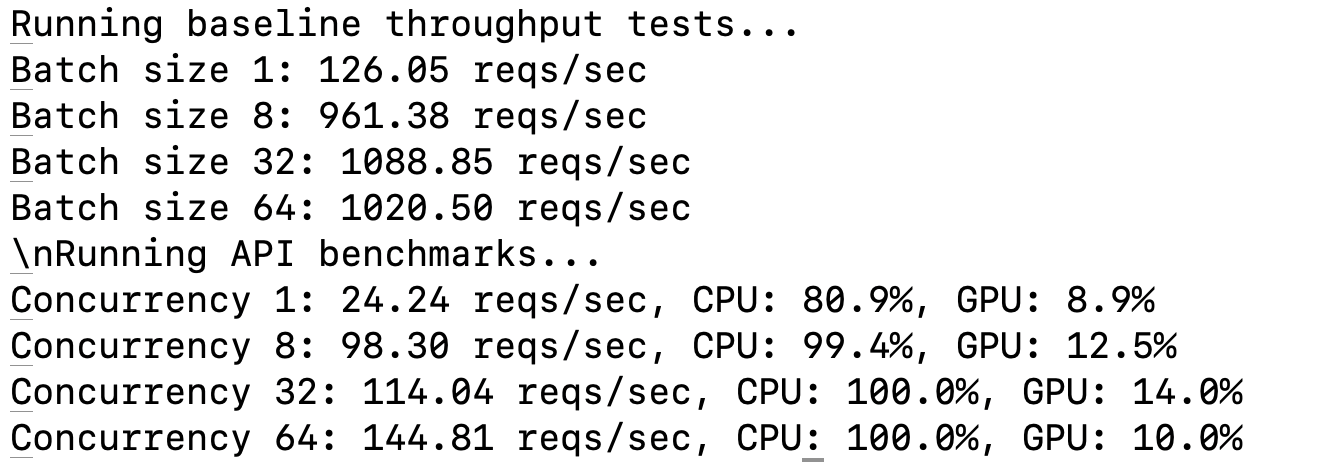
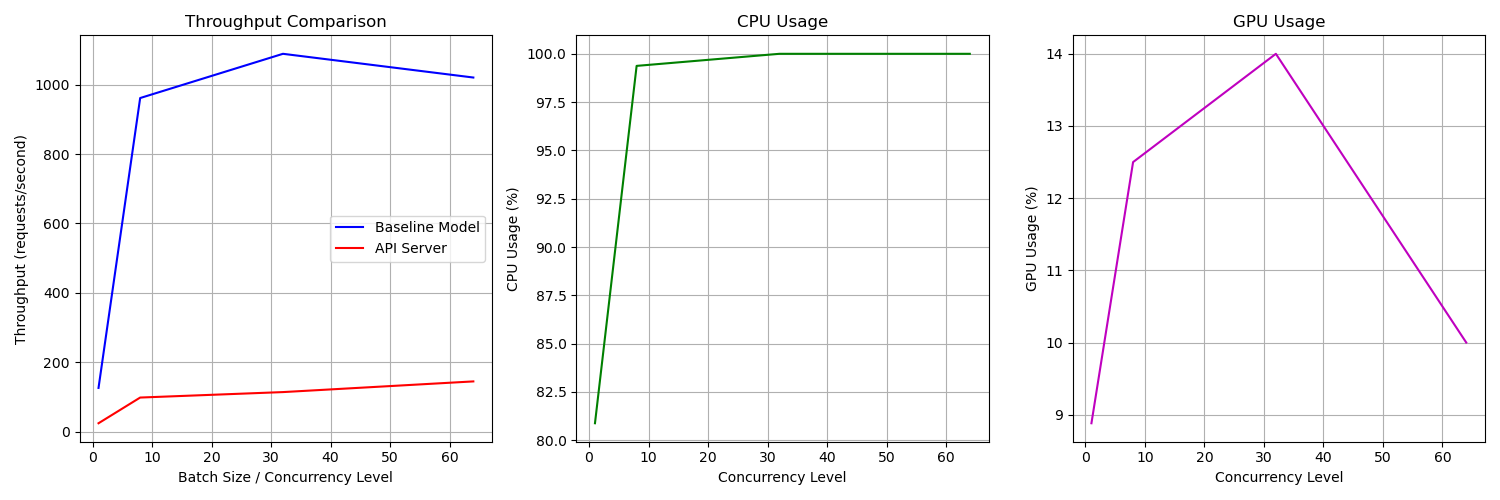
Baseline Throughput
Measure model throughput without API overhead:
batch_sizes = [1, 8, 32, 64]
for batch_size in batch_sizes:
throughput = get_baseline_throughput(batch_size)
print(f"Batch size {batch_size}: {throughput:.2f} reqs/sec 🚀")
API Performance Evaluation
Benchmark the deployed API for concurrency levels:
concurrency_levels = [1, 8, 32, 64]
for concurrency in concurrency_levels:
metrics = benchmark_api(num_requests=128, concurrency_level=concurrency)
print(f"Concurrency {concurrency}: {metrics['requests_per_second']:.2f} reqs/sec 🏆")
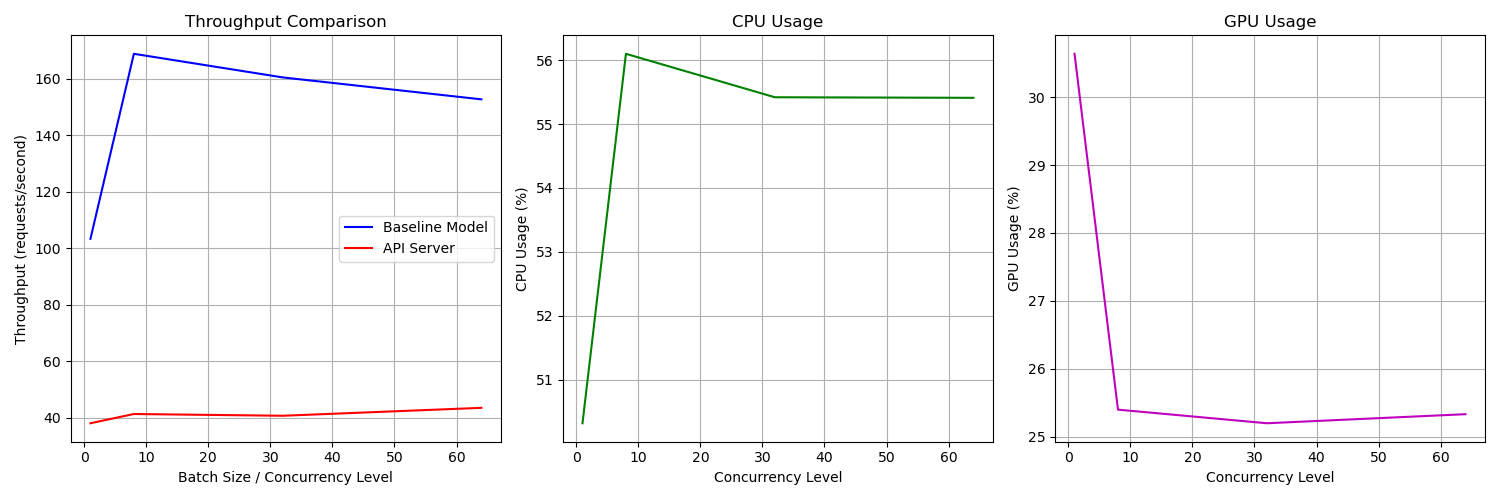
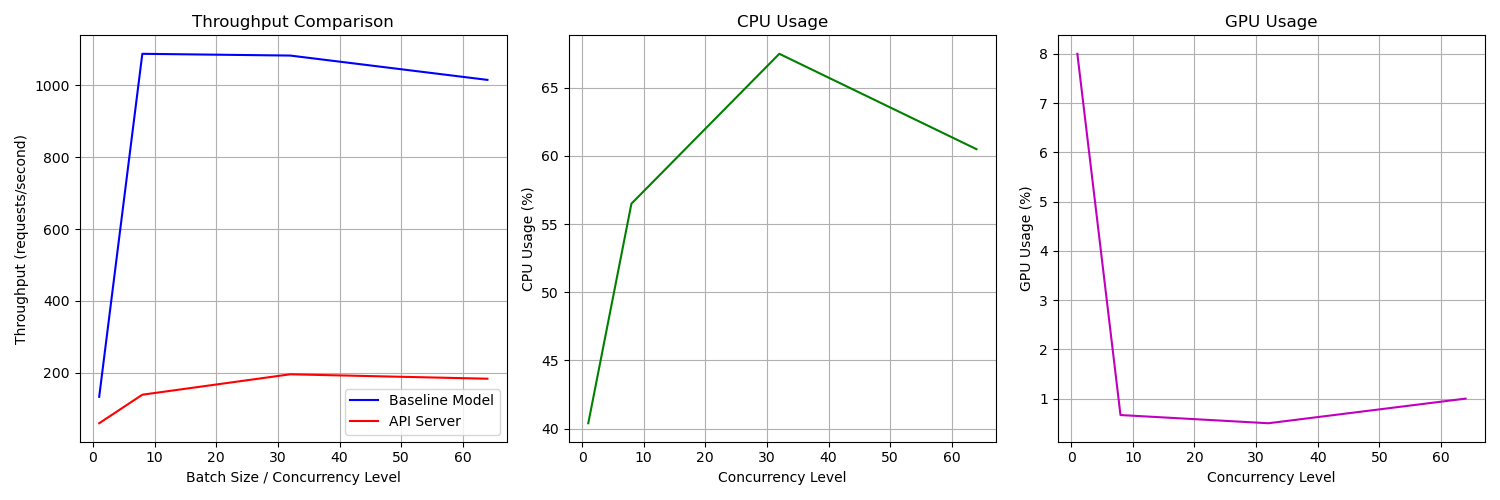
Performance Metrics
- Requests per second: Throughput achieved at different batch sizes.
- CPU & GPU Usage: Average utilization during benchmarking.
- Response Time: Average latency per request.
Sample Outputs
Server Logs
Test Client Predictions
Using test_client.py to get predictions for a test image:

Benchmarking Results
Configuration Options
1. Batching Configuration
Batching allows processing multiple requests simultaneously for improved throughput:
server = ls.LitServer(
api,
accelerator="gpu",
max_batch_size=64, # Maximum batch size
batch_timeout=0.01, # Wait time for batch collection
)
Key batching parameters:
max_batch_size: Maximum number of requests in a batch (default: 64)batch_timeout: Maximum wait time for batch collection (default: 0.01s)batching: Enable/disable batching feature
2. Worker Configuration
Multiple workers handle concurrent requests efficiently:
server = ls.LitServer(
api,
accelerator="gpu",
workers_per_device=4, # Number of worker processes
)
Server Running 4 Workers
Benchmarking
Worker guidelines:
- Start with
workers_per_device = num_cpu_cores / 2 - Monitor CPU/GPU utilization to optimize
- Consider memory constraints when setting max_workers
3. Precision Settings
Control model precision for performance/accuracy trade-off:
# Define precision - can be changed to torch.float16 or torch.bfloat16
precision = torch.bfloat16
Precision options:
half_precision: Use FP16 for faster inferencemixed_precision: Combine FP32 and FP16 for optimal performance
Deploying an LLM with OpenAI API Specification
This section covers deploying a local LLM using the OpenAI API specification, which allows for easy integration with existing tools and clients.
Installation
First, install the required dependencies:
pip install transformers accelerate
Server
Create llm_server.py to run the LLM server:
class SmolLM:
def __init__(self, device):
checkpoint = "HuggingFaceTB/SmolLM2-1.7B-Instruct"
# Initialize tokenizer and model
self.tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
self.model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
checkpoint,
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
device_map=device
)
self.model = torch.compile(self.model)
self.model.eval()
def apply_chat_template(self, messages):
"""Convert messages to model input format"""
return self.tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=False
)
def __call__(self, prompt):
"""Run model inference"""
# Tokenize
inputs = self.tokenizer.encode(
prompt,
return_tensors="pt"
).to(self.model.device)
# Generate
outputs = self.model.generate(
inputs,
max_new_tokens=512,
temperature=0.2,
top_p=0.9,
do_sample=True,
pad_token_id=self.tokenizer.eos_token_id
)
return inputs, outputs
def decode_tokens(self, outputs):
"""Decode output tokens to text"""
inputs, generate_ids = outputs
# Only decode the new tokens (exclude input prompt)
new_tokens = generate_ids[:, inputs.shape[1]:]
return self.tokenizer.decode(new_tokens[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
class SmolLMAPI(ls.LitAPI):
def setup(self, device):
"""Initialize the model"""
self.model = SmolLM(device)
def decode_request(self, request):
"""Process the incoming request"""
if not request.messages:
raise ValueError("No messages provided")
return self.model.apply_chat_template(request.messages)
def predict(self, prompt, context):
"""Generate response"""
yield self.model(prompt)
def encode_response(self, outputs):
"""Format the response"""
for output in outputs:
yield {"role": "assistant", "content": self.model.decode_tokens(output)}
if __name__ == "__main__":
api = SmolLMAPI()
server = ls.LitServer(
api,
spec=ls.OpenAISpec(),
accelerator="gpu",
workers_per_device=1
)
server.run(port=8000)
The server implementation:
- Uses
SmolLM2-1.7B-Instructmodel from HuggingFace - Implements OpenAI-compatible chat completion API
- Supports streaming responses
- Uses
BFloat16for efficient inference - Utilizes PyTorch compilation for improved performance
Client
Create llm_client.py to interact with the server:
from openai import OpenAI
# Initialize the OpenAI client
client = OpenAI(
base_url="http://localhost:8000/v1",
api_key="dummy-key"
)
# Create a streaming chat completion
stream = client.chat.completions.create(
model="smol-lm", # Model name doesn't matter
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "What is the capital of Australia?"}],
stream=True,
)
# Print the streaming response
for chunk in stream:
if chunk.choices[0].delta.content is not None:
print(chunk.choices[0].delta.content, end="")
print()

Performance Benchmarking
Create llm_benchmark.py to measure server performance:
# Constants
SERVER_URL = "http://localhost:8000/v1/chat/completions" # Update to your LLM server endpoint
CHECKPOINT = "HuggingFaceTB/SmolLM2-1.7B-Instruct"
def get_theoretical_max_throughput(max_tokens=512, time_per_token=0.01):
"""Calculate the theoretical maximum throughput based on model capabilities."""
tokens_per_second = max_tokens / time_per_token
return tokens_per_second
def benchmark_tokens_per_sec(num_requests=100):
"""Benchmark the LLM API for tokens per second."""
total_tokens_generated = 0
start_time = time.time()
for _ in range(num_requests):
prompt = "What is the capital of Australia?" # Example prompt
response = requests.post(SERVER_URL, json={"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": prompt}]})
if response.status_code == 200:
try:
output = response.json()
# Adjust the parsing logic based on the actual response format
if 'choices' in output and output['choices']:
generated_text = output['choices'][0]['message']['content']
total_tokens_generated += len(generated_text.split()) # Count tokens
else:
print(f"Unexpected response format: {output}")
except (KeyError, IndexError, ValueError) as e:
print(f"Error parsing response: {e}")
print(f"Response JSON: {response.json()}")
else:
print(f"Error: {response.status_code}")
print(f"Response Text: {response.text}")
end_time = time.time()
total_time = end_time - start_time
tokens_per_sec = total_tokens_generated / total_time if total_time > 0 else 0
theoretical_max = get_theoretical_max_throughput()
return tokens_per_sec, theoretical_max
def run_benchmarks():
"""Run the benchmark and print results."""
tokens_per_sec, theoretical_max = benchmark_tokens_per_sec(num_requests=100)
print(f"Tokens per second: {tokens_per_sec:.2f}")
print(f"Theoretical maximum tokens per second: {theoretical_max:.2f}")
print(f"Efficiency: {tokens_per_sec / theoretical_max * 100:.2f}%")
# Plotting the results
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
plt.bar(['Actual Throughput', 'Theoretical Max'], [tokens_per_sec, theoretical_max], color=['blue', 'orange'])
plt.ylabel('Tokens per second')
plt.title('Tokens per Second Benchmarking')
plt.ylim(0, max(theoretical_max, tokens_per_sec) * 1.1) # Set y-limit to 10% above the max value
plt.grid(axis='y')
plt.savefig('llm_benchmark_results.png')
plt.show()
Benchmarking Results
After running the benchmark script:

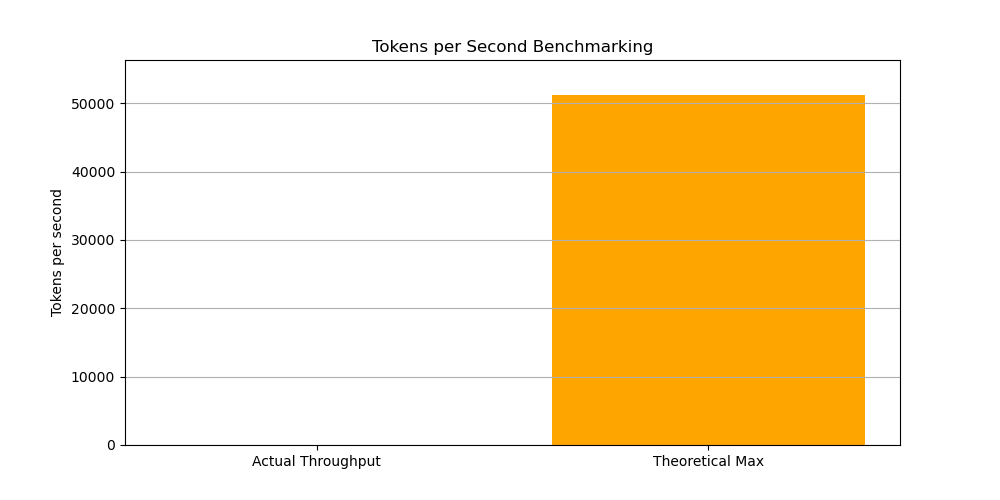
The benchmark:
- Measures actual tokens per second vs theoretical maximum
- Calculates efficiency percentage